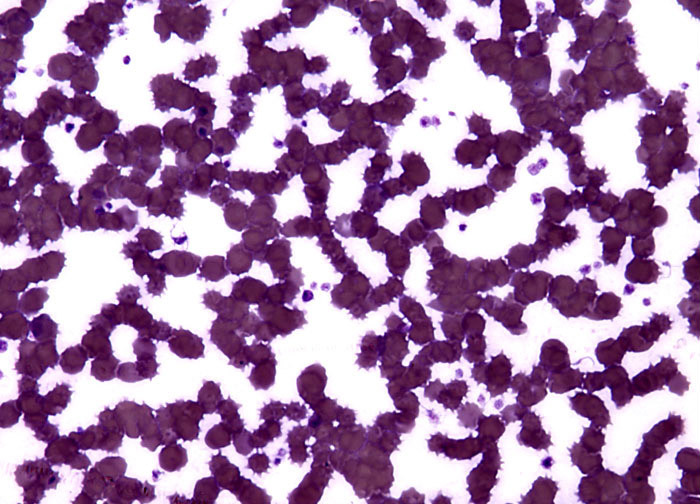
Burr Cell Uremia at 40x Magnification
Uremia is a condition in which urea and other nitrogenous substances accumulate to an abnormally high level in the blood. Symptoms of uremia often initially include fatigue, loss of appetite, edema, excessive thirst, and decreased concentration, and progression of the condition may lead to a rapid pulse, anemia, diarrhea, convulsions, discoloration of the skin, coma, and even death. Uremia is characteristically related to the inability of the kidneys to expel wastes via urine, but the underlying cause responsible for the limited function of the important organs can vary greatly. The condition may originate from, for instance, kidney damage associated with various diseases, such as diabetes mellitus or glomerulonephritis, or from a blockage of urine related to an enlarged prostate gland or kidney stones. Some cases of uremia have also been associated with abnormal red blood cells, such as echinocytes, which are often better known as burr cells.















