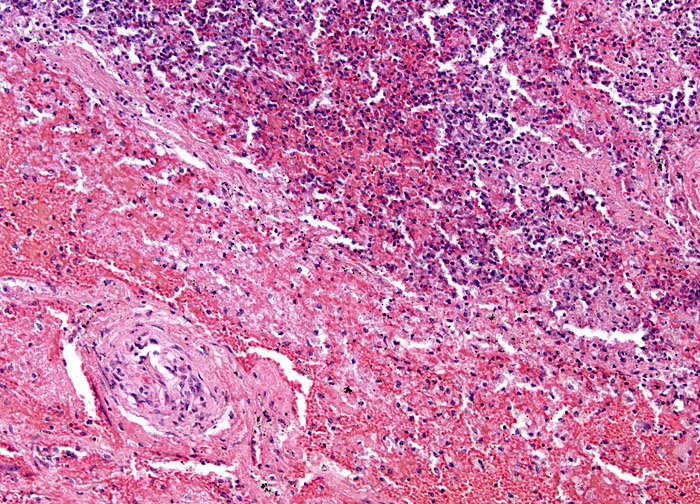
Lung Abscess at 10x Magnification
Over time, most lung abscesses rupture, emptying their contents into one of the bronchi, from which it can be coughed up, or into the pleural cavity, resulting in what is known as empyema. The spread of the pus contained in an abscess can also cause bronchopneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. By administering antibiotics in a timely manner, rupture and further dissemination of infection can often be avoided. Accordingly, patients should quickly seek medical attention when they notice the symptoms of a lung abscess, which may develop acutely or gradually. Signs of the condition frequently include fever, night sweats, malaise, appetite loss, and coughing up sputum. The sputum associated with a lung abscess may be streaked with blood or have a foul odor, especially if the causative organism is an anaerobic bacterium, such as Staphylococcus aureus.













