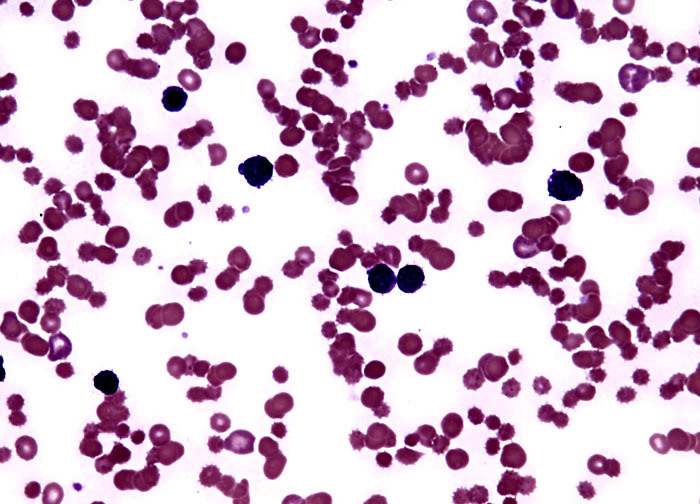
Lymphocytic Leukemia at 40x Magnification
The term leukemia is used to describe a group of neoplastic diseases primarily involving the bone marrow that are characterized by an abnormal proliferation of white blood cells (leukocytes). In acute lymphocytic leukemia and other acute varieties of the cancer, the onset of the disease is sudden and it progresses rapidly, whereas chronic leukemias develop gradually and slowly worsen over time. As suggested by its name, a lymphocytic leukemia is one that affects lymphocytes, which in a healthy individual comprise about 20 to 30 percent of the total white blood cell count. Normally, lymphocytes and other mature white blood cells form from stem cells in the bone marrow. The source cells of lymphocytes, however, which are known as lymphoblasts, multiply uncontrollably in the bone marrow of patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia, interfering with the production of normal blood cells.













