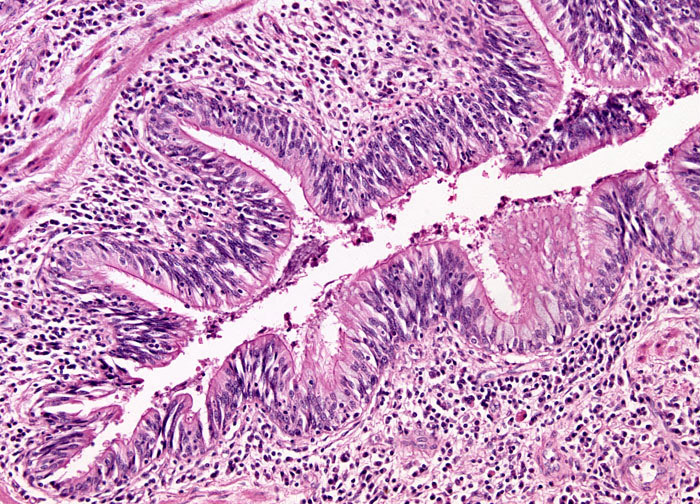
Bronchiectasis at 10x Magnification
Bronchiectasis is an abnormal, permanent dilation of the bronchial tubes in the lungs. The condition can result from a number of different causes. For example, obstructions, such as those posed by foreign objects (often accidentally ingested during childhood) or tumors, can prevent the elimination of fluid emissions from the bronchi, resulting in their expansion. Following initial dilation, the tubes continue to swell with accumulated materials even after the obstruction is removed. Bronchiectasis is also frequently associated with pneumonia, whooping cough, measles, or other infections that can inflame and weaken the walls of the bronchi. Over the course of several infections, the walls of the tubes can deteriorate to such an extent that the elastic and muscle fibers they contain are damaged to such an extent that dilation occurs. Some inherited conditions, especially cystic fibrosis, are known to be linked to bronchiectasis as well.













