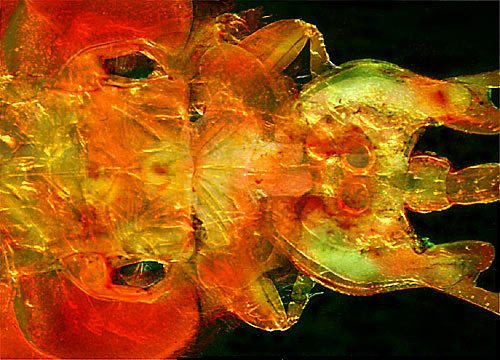
Fish Louse
These crustacean parasites are infamous for their aggressive attachment and feeding behavior, grasping tightly onto their hosts using small spines, hooked appendages, and a pair of large suckers. A feeding louse will pierce and inject digestive enzymes into the skin or gills of a fish using a stylet — a pointed, needlelike structure — and then suck blood, mucus and enzyme-liquefied body fluids from the host. Constant piercing of the fish skin or gills can cause inflammation and leave the damaged site vulnerable to infection by opportunistic bacteria.













