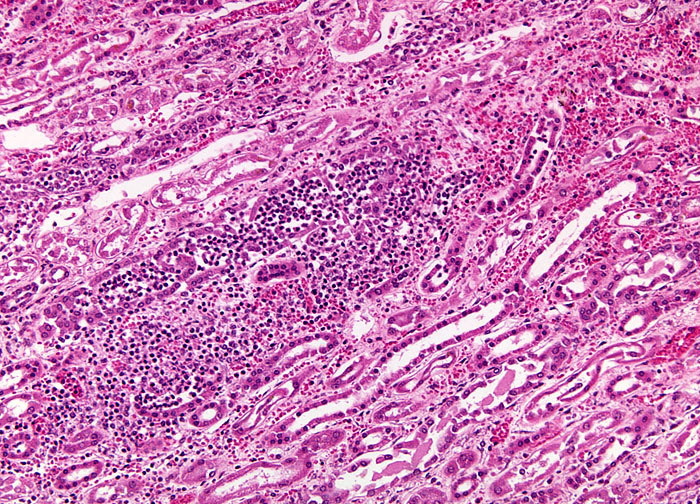
Hematogenous Pyelonephritis at 10x Magnification
Due to its bacterial origin, hematogenous pyelonephritis is typically highly responsive to antibiotics. When antibiotics are utilized, improvement in symptoms, which may include pain in the flanks, groin, or abdomen, discomfort or burning sensation during urination, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and cloudy urine, usually improve quickly. Patients should be careful to remember that antibiotics should always be taken as long as is prescribed even if symptoms have already disappeared. If pyelonephritis is left untreated, the acute form of the disease may eventually lead to chronic pyelonephritis and can cause permanent renal damage.













