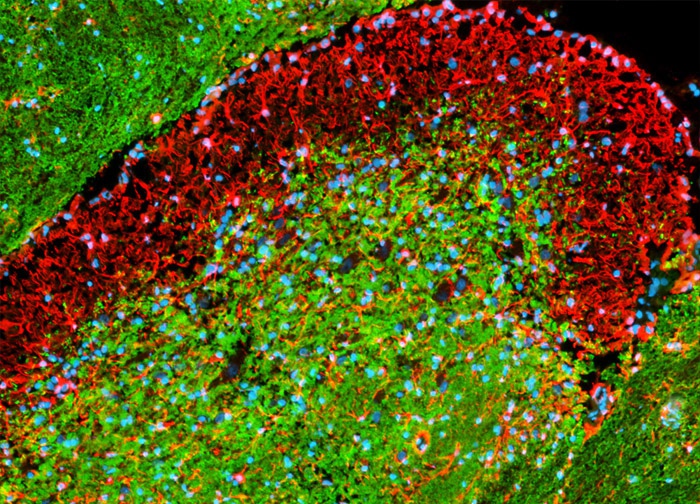
Immunofluorescently Labeled Myelin and Astroglia in a Sagittal Section of Rat Brain Tissue
Immunofluorescence was utilized to target myelin and astroglia in a sagittal section of rat brain tissue. First, the specimen was fixed, permeabilized, blocked with 10-percent normal goat serum, and treated with a cocktail of mouse anti-myelin CNPase and rabbit anti-GFAP primary antibodies. Next, to visualize the primary targets, the tissue section was treated with goat anti-mouse and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (IgG) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 and Alexa Fluor 568, respectively. Finally, cell nuclei were labeled with Hoechst 33342. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.













