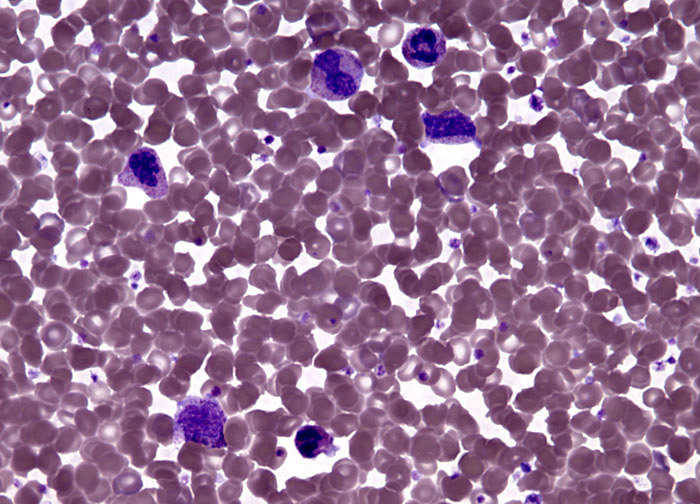
Polycythemia at 40x Magnification
Polycythemia is a condition characterized by an abnormal proliferation of erythrocytes (also known as red blood cells) in the blood. This increased presence of erythrocytes thickens the blood and slows its flow through the body, as well as elevates the risk of blood clot formation. Consequently, polycythemia can sometimes culminate in pulmonary embolism, stroke, heart attack, or other thrombosis-related events. More often symptoms include headache, fatigue, shortness of breath, light-headedness, itchiness, easily bruised skin, bleeding, and hypertension. Diagnosis of polycythemia usually involves a physical examination, patient history, and close study of the blood, which may encompass measurements of oxygen levels, the hormone erythropoietin, and erythrocyte mass. Occasionally imaging studies are also considered necessary in order to help determine what factors may have instigated the condition.













