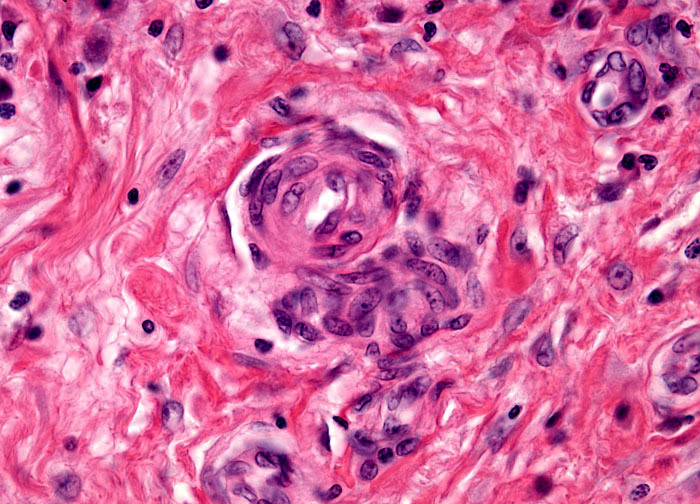
Sarcoidosis at 40x Magnification
Many individuals with sarcoidosis do not require any treatment for the disease. When symptoms are severe, however, or when the disease affects the nervous system, therapy may be advisable. The primary form of treatment for sarcoidosis is the administration of a corticosteroid, frequently prednisone, which suppresses inflammation. Generally, this form of treatment results in significant improvement, but cessation of use typically results in the reappearance of symptoms. Thus, due to the long course of the disease, which can extend as long as 36 months, corticosteroid treatment would necessarily be required for an extensive amount of time. However, the possibility of adverse side effects from corticosteroid usage, such as ulcers, calcium loss, and high blood pressure, increases when the synthetic hormone is taken for lengthy periods. Consequently, patients should carefully consider the possible problems of treatment as well as its benefits before electing to undertake it.













