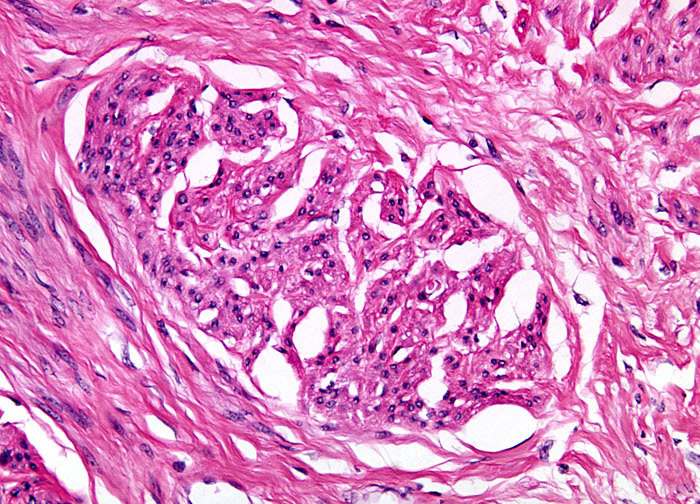
Uterine Leiomyoma at 20x Magnification
A leiomyoma is a benign tumor that originates in smooth muscle tissue, such as that found in the intestinal walls and the heart. When present in the uterus, leiomyomas are commonly referred to as fibroids, a term that reflects the fact that in addition to smooth muscle, the growths characteristically contain fibrous connective tissue. It is generally believed that this fibrous material is a result of the degeneration of muscle tissue. Leiomyomas tend to be firm to the touch and well circumscribed. When associated with the uterus, which is the organ most commonly affected by the growths, leiomyomas are usually classified as one of several different types based upon their location. Growths positioned just under the uterine serosa are referred to as subserosal leiomyomas, whereas those found just beneath the endometrium are called submucous leiomyomas. Both of these types of tumors may be sessile or extended from a stalk (peduncular). Intramural leiomyomas, however, which are those that predominantly occur in the myometrium, are always attached directly to one or more tissues.













