Stereomicroscopy
Considering the wide range of accessories currently available for stereomicroscope systems, this class of microscopes is extremely useful in a multitude of applications. Stands and illuminating bases for a variety of contrast enhancement techniques are available from all of the manufacturers, and can be adapted to virtually any working situation. There are a wide choice of objectives and eyepieces, enhanced with attachment lenses and coaxial illuminators that are fitted to the microscope as an intermediate tube. Working distances can range from 3-5 centimeters to as much as 20 centimeters in some models, allowing for a considerable amount of working room between the objective and specimen.
Review Articles
Introduction to Stereomicroscopy
Perception of depth and contrast is critical to the interpretation of specimen structure.
Specimen Contrast in Optical Microscopy
Using phase-related optical techniques to increase specimen contrast.
Stereomicroscopy Fluorescence Illumination
Fluorescence Illuminators enable examination of large specimens in stereomicroscopy.
Reflected (Episcopic) Light Illumination
Techniques currently in use to illuminate specimens observed with reflected light.
Oblique Illumination
Illumination directed from a single azimuth that strikes the specimen at an oblique angle.
Darkfield Illumination
Darkfield observation in stereomicroscopy requires a stand containing a reflection mirror.
Interactive Tutorials
-

Focus and Alignment of Mercury and Xenon Arc Lamps
Explore alignment and focusing of the arc lamp in a mercury or xenon burner, which simulates how the lamp is adjusted in a real microscope.
-
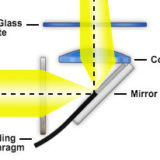
Oblique Coherent Contrast Illumination
Enhancing contrast in stereomicroscopy with transmitted light.
-

Stereomicroscopy Fluorescence
Explore the light paths in Nikon's SMZ1500 stereomicroscope equipped for fluorescence illumination using an intermediate tube and external lamphouse.
-
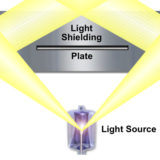
Toroidal Mirrors
Explore how mirror shape affects the amount of light entering the objective in darkfield stereoscopic microscopy. This tutorial demonstrates lightpath differences between conventional and toroidal mirrors.
Galleries
Selected Literature References
Specimen Contrast in Microscopy
Examine the origins of contrast in a wide spectrum of specimens.
Stereomicroscopy
Long working distance, low magnification microscopes for stereoscopic observation.
Contributing Authors
Paul E. Nothnagle - Avimo Precision Instruments, 78 Schuyler Baldwin Drive, Fairport, New York, 14450.
William Chambers - Microscopy Consultant, Nikon Instruments Inc., Melville, New York 11747.
Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.














