Differential Interference Contrast
An excellent mechanism for rendering contrast in transparent specimens, differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy is a beam-shearing interference system in which the reference beam is sheared by a minuscule amount, generally somewhat less than the diameter of an Airy disk. The technique produces a monochromatic shadow-cast image that effectively displays the gradient of optical paths for both high and low spatial frequencies present in the specimen. Those regions of the specimen where the optical paths increase along a reference direction appear brighter (or darker), while regions where the path differences decrease appear in reverse contrast. As the gradient of optical path difference grows steeper, image contrast is dramatically increased.
Review Articles
de Sénarmont Bias Retardation in DIC Microscopy
DIC with a fixed Nomarski prism and a simple de Sénarmont compensator.
de Sénarmont DIC Microscope Configuration
de Sénarmont compensators offer more accuracy for introduction of bias retardation.
Reflected Light DIC Microscopy
Examination of highly reflective specimens in DIC microscopy with epi-illumination.
Specimen Contrast in Optical Microscopy
Using phase-related optical techniques to increase specimen contrast.
Interactive Tutorials
-
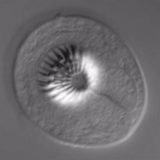
Bias Retardation Effects on Specimen Contrast
Explore the effects of varying bias retardation on specimen contrast.
-
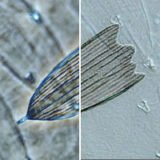
Comparison of Phase Contrast & DIC Microscopy
Examples of the same specimen viewed in either phase contrast or DIC.
-

Nomarski Prism Action in Polarized Light
Variations in prism geometry yield unique interference patterns in polarized light.
-

Optical Sectioning in Reflected Light DIC
Optical sectioning of reflected light specimens (semiconductors).
-
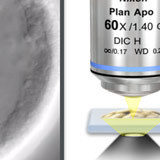
Optical Sectioning with de Sénarmont DIC Microscopy
At high numerical apertures, DIC can be used for optical sectioning.
-
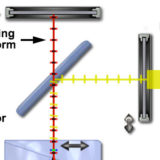
Wavefront Relationships in Reflected Light DIC Microscopy
Observe how light waves travel through a reflected light DIC microscope.
-
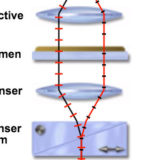
Wavefront Relationships in de Sénarmont and Nomarski DIC
An interactive comparison of wavefronts in these complementary techniques.
Galleries
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)
Compare specimen contrast using these complementary imaging techniques.
Image Comparisons • Movies
Selected Literature References
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC)
Contrast enhancement using interference of polarized light wavefronts.
Specimen Contrast in Microscopy
Examine the origins of contrast in a wide spectrum of specimens.
Contributing Authors
Douglas B. Murphy - Department of Cell Biology and Anatomy and Microscope Facility, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, 725 N. Wolfe Street, 107 WBSB, Baltimore, Maryland 21205.
Stanley A. Schwartz - Nikon Instruments, Inc., 1300 Walt Whitman Road, Melville, New York, 11747.
Edward D. Salmon - Department of Cell Biology, The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27599.
Kenneth R. Spring - Scientific Consultant, Lusby, Maryland, 20657.
Matthew Parry-Hill, Robert T. Sutter, and Michael W. Davidson - National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310.













