
Are you on X?
Follow Nikon Instruments for microscopy news and trends, updates on new products, and information on contests and promotions.
November 29, 2016, via Nature Methods
Check out our new application note in Nature Methods discussing how the Nikon Ti2 inverted research microscope is ideally suited to high content imaging applications. The unprecedented 25 mm field of view of the Ti2 (camera port) provides about a two-fold improvement in imaging area over its predecessor, drastically increasing system throughput and speeding up discovery.
Learn More @ Nature Methods
November 28, 2016, via Nikon Instruments
We hope everybody is excited about the upcoming The American Society for Cell Biology annual meeting being held at San Francisco’s Moscone Center. Please join us at Booth 623 from December 4-6 to see our new Ti2 inverted microscope and other exciting imaging solutions.
Learn More @ Nikon Instruments
November 23, 2016, via Medical Xpress
Researchers from UCSF and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign have succeeded in pausing the development of mouse blastocysts for up to one month via inhibition of the mTOR protein. Briefly paused embryos retained the ability to develop normally. This strategy also worked on cultured embryonic stem cells, inducing a pluripotent state that can last for weeks in vivo. Their research has implications in a variety of fields, including ageing, cancer, assisted reproduction, and more.
Learn More @ Medical Xpress
November 22, 2016, via Nature Methods
New research published in Nature Methods details the development of a bright new red fluorescent protein – mScarlet – with an excitation maximum of 569 nm and emission maximum of 594 nm. mScarlet is highly monomeric and about 3.5 times brighter than mCherry. Additionally, mScarlet has a pKa of 5.3, making it tolerant of acidic environments.
Learn More @ Nature Methods
November 21, 2016, via Nikon Instruments

We hope that everybody had a wonderful time at this year’s Society for Neuroscience 2016 Annual Meeting! If you didn’t get a chance to see our new inverted Ti2 microscope in person, check the link to see what you missed.
Learn More @ Nikon Instruments
November 18, 2016, via Nature Communications
Research published in Nature Communications details the relationship between the shape of epithelial cells and microtubule organization. Super-resolution imaging of microtubules and e-cadherin was performed using 3D Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM).
Learn More @ Nature Communications
November 16, 2016, via Nature Biotechnology
New research published in Nature Biotechnology details a method for optimizing spatial resolution during acquisition of light sheet microscopy data. An automated program corrects for mismatches between the plane of light sheet illumination and that imaged by the detection objective in real time, demonstrated by imaging of entire zebrafish and fly embryos. Imaging was performed using a Nikon 16x water-dipping objective.
Learn More @ Nature Biotechnology
November 10, 2016, via Phys.org
Lasers and… anti-lasers? Researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have constructed a laser that also acts as an anti-laser. A laser emits coherent light - anti-lasers absorb coherent light. A single device that does both may seem paradoxical, but the authors believe the technology may be used to make high sensitivity light detectors, or even photonic integrated circuits. To learn more check out the Phys.org article.
Learn More @ Phys.org
November 09, 2016, via Nikon Instruments

Introducing Nikon's latest imaging innovation- the Eclipse Ti2 Inverted Microscope System. The Ti2 raises the bar for core imaging capability, delivering an unprecedented 25mm field of view, as well as improved stability and usability. To learn more, visit www.seemorethanbefore.com and stop by Nikon's booth at the upcoming Society for Neuroscience Annual Meeting (Nov. 13-16).
Learn More @ Nikon Instruments
November 08, 2016, via Nature Scientific Reports
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have demonstrated super-resolution localization microscopy imaging of endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells. Labeling was performed using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing to add the photoconvertable fluorescent protein Dendra2. This method can in principle be used to label transcription factors for live cell super-resolution as well. Imaging was performed on a Nikon Ti inverted research microscope system with Perfect Focus. Check out the open access Scientific Reports article to learn more.
Learn More @ Nature Scientific Reports
November 07, 2016, via Nature Protocols
Researchers at ETH Zürich have published a new method in Nature Protocols for axially confined photoconversion of the fluorescent protein Dendra2 in single cells – demonstrating the concept in developing zebrafish embryos. This method uses a specialized filter plate and the process of ‘primed conversion’ to convert Dendra2 to a red emitting form using 488 nm and 730 nm beams that intersect only at a common focal point.
Learn More @ Nature Protocols
November 04, 2016, via Nikon Instruments
Are you attending the Society for Neuroscience 2016 Annual Meeting? If so, come find Nikon at Booth #2513 from November 13-16! Our latest imaging solutions will be on display, and all will be revealed...
Learn More @ Nikon Instruments
November 03, 2016, via nic.med.harvard.edu

We would like to extend our thanks to everybody who attended the Nikon Imaging Center at Harvard Medical School 15th Anniversary Symposium. Here's to the next 15 years!
Learn More @ nic.med.harvard.edu
October 31, 2016, via Light: Science & Applications
A new open-access research article in the journal Light: Science & Applications details a new Fluorescence Polarization Microscope (FPM) design for super-resolution imaging of the dipole orientations of overlapping single fluorophores in sub-diffraction limited volumes. Using this new technique, they’ve demonstrated that the dipole of actin monomers is perpendicular to the actin filament, and radially distributed in septin complexes in live yeast cells. Imaging was performed on a Nikon Ti-E motorized inverted research microscope.
Learn More @ Light: Science & Applications
October 27, 2016, via PHYS.ORG
It is well known that the human brain has a limited ability to compensate for nerve cell loss, but new research shows that embryonic neurons transplanted into the visual cortex of adult mice can mature into pyramidal cells – restoring several lost functions. Check out the Phys.org article to learn more.
Learn More @ PHYS.ORG
October 26, 2016, via Nature Methods
Researchers at the Janelia Research Campus have developed new photoactivatable dyes for improved live cell single-particle tracking and localization microscopy experiments. The new photoactivatable dyes are derived from existing Janelia Fluor (JF) dyes - known for their increased brightness, photostability, small size, and cell permeability. To learn more, check out the article in Nature Methods.
Learn More @ Nature Methods
October 19, 2016, via Nikon Small World
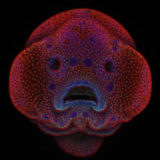
Nikon Instruments Inc. today announced the winners of the 42nd annual
Nikon Small World Photomicrography Competition, awarding first place to
Oscar Ruiz, Ph.D. for his microscopic view of the facial development of
a four-day-old zebrafish embryo. Fittingly, Nikon unveiled Dr. Ruiz’s zebrafish “selfie” win first on Instagram this morning, giving followers the first look at the winning images. The full winner gallery can now also be viewed on www.nikonsmallworld.com.
Learn More @ Nikon Small World
October 13, 2016, via Nature Scientific Reports
A new open access article in Scientific Reports details the role of extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness in regulating breast cancer cell activity by testing cell growth on a variety of 2D and 3D substrates. Researchers found that the highest proliferation rates occurred in the softest 3D hydrogels tested – providing more evidence for the need of 3D culture systems recapitulating the native microenvironment in order to reveal disease-relevant phenotypes. Gels were imaged using a Nikon Eclipse Ni-U upright research microscope.
Learn More @ Nature Scientific Reports
October 12, 2016, via PHYS.ORG
Many people in the microscopy world are familiar with quantum dots – semiconductor nanocrystals with well-defined light emitting properties – as fluorescent labels. Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory have demonstrated how quantum dot-based solar panels can be scaled up for practical use, large enough to be used as a building window when used in luminescent solar concentrators (LSC). Quantum dots in LSCs absorb photons and emit light at a lower energy, guided by total internal reflection to the edges of the device, where they are collected by photovoltaic cells.
Learn More @ PHYS.ORG
October 11, 2016, via Medical Xpress
A team of researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard realized a major milestone in 3D bioprinting with the construction of a working proximal tubule – a key component of kidney nephrons – made of human epithelial cells. They hope to use these engineered tubules as models of human kidney function, providing a highly relevant system for pre-clinical drug response testing.
Learn More @ Medical Xpress


















